Most browsers provide a private browsing mode, allowing users to protect their privacy. Google Chrome calls this feature the Incognito mode. But, how safe is incognito browsing? Is going “incognito” really private? Let us unravel some of the misconceptions.
What is Incognito Mode?
According to Wikipedia: “Private browsing is a privacy feature in some web browsers. When operating in such a mode, the browser creates a temporary session that is isolated from the browser’s main session and user data.”
Apple was the first one to introduce the private browsing feature with the Safari browser. Google coined the term “Incognito Mode” to describe the same feature in Chrome.
Private browsing works similarly in most modern browsers, but it is known by different names. Opera has the Private Mode feature. Edge calls it InPrivate browsing. In the case of Firefox and Safari, it is simply called Private browsing. Since Google Chrome is the most used browser in the world, we will use the Incognito mode as an example in this article.
How to Use Incognito Mode?
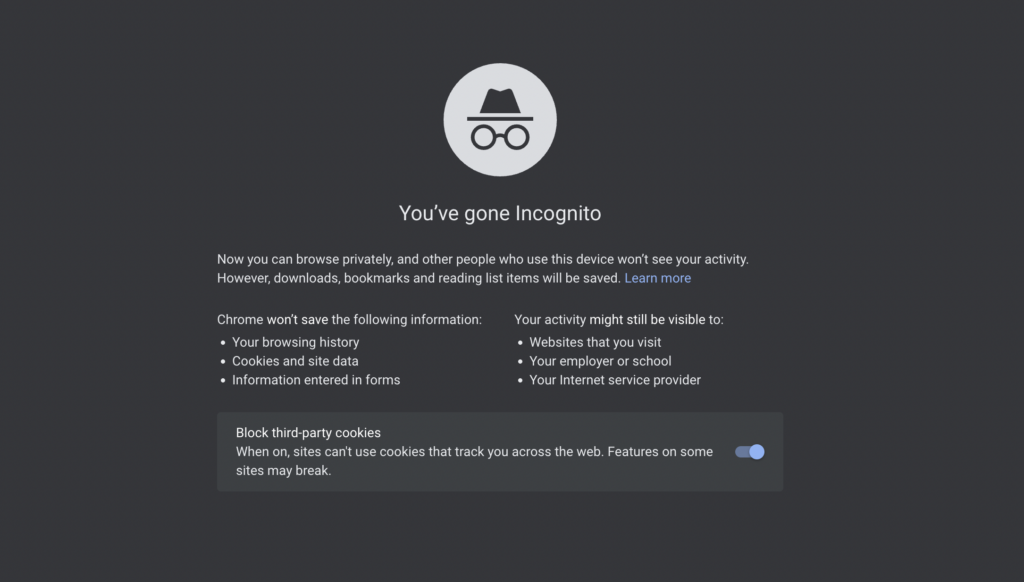
Right-click on the Chrome app icon in the taskbar and select “New incognito window” to go directly to private browsing mode. Alternatively, launch Google Chrome and press Ctrl + Shift + n on Windows (or Cmd + Shift + n on macOS) to open a new Chrome window in incognito mode. The feature has a black background with some general guidelines.
Chrome incognito mode also has a new feature. At the bottom is a switch to block the use of cookies by third-party websites. Cookies are small packets of data that websites use to track you on other sites.
How Incognito Mode Operates?
When browsing the Internet in this “anonymous mode”, the primary task of the browser is not to store data locally on your computer. By closing the incognito window, your browser deletes the following:
Browsing history: all the websites you visit, whether you were signed in or not.
Internet searches: all searches you have performed. Your search queries are still being recorded by the relevant server. Privacy-oriented search engines do not track your searches at all, but record them in your browsing history unless you use private browsing.
Cache and cookies: cover authentication of sites you have signed in to, site-specific settings and preferences, parts of web pages saved for faster loading, and more.
Login information: any usernames or passwords you enter.
Form data: any information such as the name and address you may have entered on the form.
Website Permissions: any permissions you give to a website such as access to a location or microphone, will not be saved (because the cookies that websites use to store such information are not saved).
While using incognito mode, you are not signed in to your Google Account unless you do so manually, and none of the activity from the incognito browser session is associated with your Google Account. This is true even if you signed in to Google through the usual window next to the incognito window.
The moment you close incognito mode, your browser will forget that the browsing session ever happened. How practical! It will instantly clear your browsing history, cache, cookies, and no one with access to your computer can find out which websites you have visited. It is no wonder this option gives users a sense of privacy.
How Safe is Incognito Mode?
Note that incognito mode does not provide full anonymity. When you open an Incognito window, it actually states that your browsing activity might still be visible to others. It provides no protection against government surveillance or hackers.
As mentioned above, incognito mode or private browsing protects your browsing history from those who may have physical access to your computer. However, a few entities can still see what you are doing online.
- The websites you visit: They can and most likely are still being tracked. For example, Google records your search history if you sign in unless you have paused Web activity and Apps in the My Google Activity dashboard.
- Internet Service Provider: Your ISP can track your web browsing, thanks to the IP address assigned to you.
- Network Administrators: If you use your office or school computer, authorities may monitor your browsing activity.
- Hackers and data intermediaries: If hackers have access to your computer, the incognito mode will not detract them from getting access to your information. Alternatively, provided that someone can intercept your data, they should have a similar level of access to your ISP.
When to Use Incognito Mode?
Private browsing is useful if:
- you do not want, for example, other family members or co-workers to know what you are looking at online. Deleting browsing history manually is tedious work, and an action people often forget to take.
- when you want to log in to the same service using two separate accounts.
- when using public devices or computers (this way, closing the private session will remove all traces of your online activity).
Are There Any Alternatives to Incognito Mode?
What should you use instead of incognito mode or private browsing, if you want to maintain the privacy of your browsing activity both locally and online?
Private browsing mode with VPN. VPNs (or virtual private networks) are designed to encrypt network traffic by masking your IP address assigned to you by your ISP. It also changes your location to another part of the world. VPN is often used to access the geo-restricted content on popular Internet streaming sites and circumvent geo-located censorship.
In case you want to search the Internet more privately, VPN is probably a better option. These services will mask your IP address and protect the privacy of your online activity.
Using a VPN with Incognito Mode
Since incognito mode prevents some users from seeing your browsing history, and VPN prevents all other users from accessing your data – combining these two options will significantly increase the level of privacy and security online.
Is Incognito Mode Safe From Viruses?
Certainly not. Your computer may still be infected with malware, viruses, and other forms of network threats. So, be careful which websites you visit and the files you download while using incognito mode.