As a regular internet user, from time to time you come across websites with certain errors. Most of these errors come with an error code that is difficult for the average web user to understand. Our guide is here to help you demystify these problems and find an effective solution. In this article, learn more about the 8 most common HTTP error codes and how you can solve them.
What do HTTP Error Codes Mean in General?
Before moving on to specific cases, it is helpful to have a little background on what those codes are and why you are receiving them. HTTP codes are messages that are sent to the website server and returned to the browser to indicate whether the request has been met (or can be met).
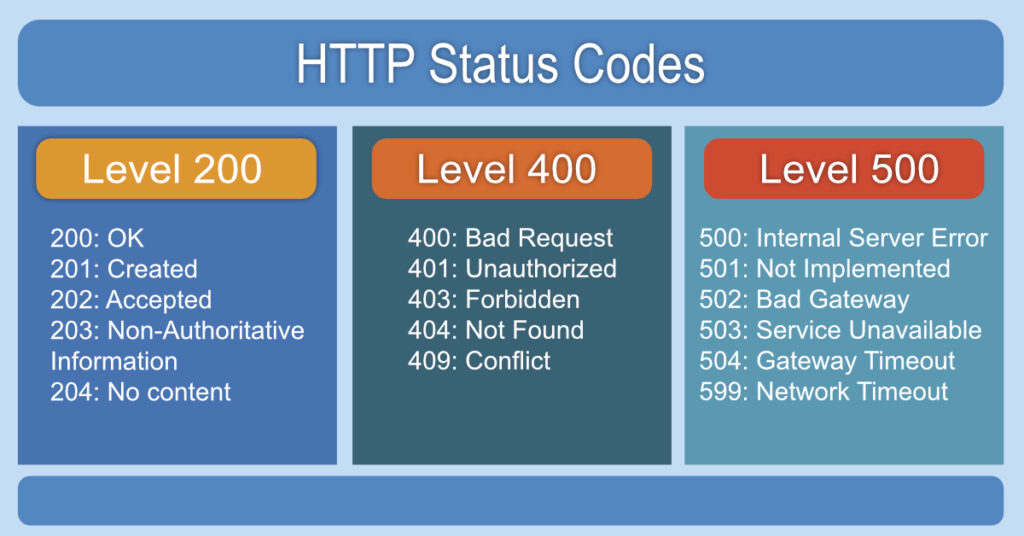
There are generally five levels:
- 100s: Informational codes indicate that the request initiated by the browser is continuing.
- 200s: Success codes returned when browser request was received, understood, and processed by the server.
- 300s: Redirection codes returned when a new resource has been substituted for the requested resource.
- 400s: Client error codes indicate that there was a problem with the request.
- 500s: Server error codes indicate that the request was accepted, but an error on the server prevented the fulfillment of the request.
Let’s now look at some of the most common ones you will encounter.
The Most Common Ways to Fix HTTP Errors
Before moving on to more specific error codes, it is important to know some of the common steps you can take to correct any errors on the site you encounter. While not true for all error codes, for the most part, your first step should be to try to refresh the page. It is quite possible that something happened while the page was trying to load and the refresh of the page will resolve the issue.
Another common solution is to double-check the website address. Possibly, you typed the URL of the web page incorrectly or added a number, letter, or symbol.
If you have also tried refreshing the page and double-checking that everything is spelled correctly, clearing the cache is the next best step. It is a simple step that will not affect your browsing experience.
Several other common fixes also revolve around disconnecting the VPN. While this is not quite common, the site may be affected by a VPN you could be using. Try disconnecting and verifying that the site is loading. Or how about trying to load a site in incognito mode or using a different browser?
Which are the 8 Most Common HTTP Error Codes?
“HTTP Error 401 – Unauthorized (Authorization Required)”
In case you see this HTTP error code, it probably means that the page you are trying to visit requires a user ID and password. If this is a page you have already signed in to and you still see the error, the user credentials you entered are invalid. The repair could only require a return to the site’s main page, locating the login screen, and re-entering valid credentials. Try:
- Reloading the page, clearing the cache, or closing and reopening the browser (then try signing in again).
- If you are sure that your credentials are working and the problem is not on your side, contact the site administrator for assistance.
“HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden”; “HTTP Error 403 – Denied Access”
When you see this error on a page, it means that you are on a page for which you do not have permission to view. There are several reasons why you may encounter this message, but the general conclusion is “this site is not for you”. To avoid this error,
- make sure you are accessing the correct URL.
- make sure all the required logins have been entered to ensure you have access.
- other common fixes, like refreshing your browser and clearing your cache are your next best steps.
“HTTP Error 404 – Page Not Found”
This is probably the most famous of the 4xx status codes as it appears regularly whenever your browser asks you to visit a page that its server cannot find. You will probably see this when you have clicked on an incorrect link, typed in a webpage URL incorrectly, or redirected it incorrectly. If you see this error, there is a strong possibility that the error is on the user’s side and not on the website itself. Resolving this issue is as simple as:
- Verify that you entered the URL correctly.
- Try searching the Google webpage to see if the page has been recently moved.
- Scroll one directory level in the URL to see if the issue is resolved.
“HTTP Error 408 – Request Timeout”
Although not as common, a 408 error means that the site was loading longer than the server was willing to wait. As a result, a 408 error was delivered to the browser. The cause is something as basic as typing or loading the wrong URL. When you see this error:
- Verify that the URL is typed correctly (pay attention to the spelling of the domain name, the position of the inverted slash, etc.).
- Make sure they are also spelled/inserted correctly. Try searching the site through different browsers and see if you can find the site this way.
“HTTP Error 500 – Internal Server Error”
It is important to note that errors in the 5xx range are generally based on a problem with the website and/or its server. In other words, the problem is more than a spelling mistake with the URL. If you see this message, the site may have encountered some sort of unexpected error while trying to reach the server.
Resolving this error must involve the webmaster who needs to resolve the errors with the server, site code, database, etc. This could also be due to high traffic. Refresh the page from time to time.
“HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway”
When you see a 502 Bad Gateway error, it is a good indication that the problem is server-based and not specific to your setup. This means that no matter which device or operating system you use to try to visit the website, the same error will occur. Generally, this error occurs when two servers do not talk to each other. In some cases, a 502 error may occur because your browser of choice thinks there is a problem.
As a solution to the problem:
- Start by trying to refresh the page.
- The next best option is to try another browser or other device (this will help determine where the problem exists and if something is happening on the user side).
- Separately, try restarting your computer to see if it provides a quick fix.
- Some internet searchers have identified browser extensions as a potential cause of 502 error. If all else fails, try disabling your browser extensions one by one to see if a fix is found.
“HTTP Error 503 – Service Unavailable (Service Temporarily Unavailable)”
Whenever you see this message appear while trying to visit a website – the server is currently unavailable. In most cases, the server may be under heavy traffic or it may mean that routine maintenance is being performed.
Since the problem is not user-based, you can try to fix it by refreshing the page. These problems are probably temporary, and trying to reopen the page a few minutes later is the best way to get to the website. You can also try restarting the modem/router, as well as the device, and see if the same 503 error keeps recurring.
“HTTP Error 504 – Gateway Timeout”
If you see an HTTP error 504, this is an indication that the time for the website you are trying to visit has expired. The website and its server are not communicating properly, and as a result, this error occurs. Refresh the page to see if the problem will be resolved quickly. If not, try to solve the problem by resetting the router/modem, making sure your DNS settings are set up correctly. If the problem is not fixed, contacting the site administrator is probably the next best step.
What About Non-HTTP Errors?
Errors such as “Network Connection Refused” or “Unable to Locate Host” are just as common as these numerical errors. The first is something you will see if the site is under heavy traffic or it is being maintained. These problems are solved quickly and you can try to visit the site later. The last error is probably the result of the same problem.
However, it can also extend to a website which is not talking to its server properly. Please check the URL in both cases and give it another try.
While they may seem confusing or intimidating at first, HTTP status codes are actually very informative. When you are better acquainted with some of the most common ones, you can solve problems on your website quickly and efficiently.