Audio files are critical in entertainment, communication, and creative projects. With various formats available, knowing when to use MP3, WAV, or FLAC can help you achieve the best quality and compatibility for your needs. In this guide, we will dive into these three popular audio formats, explaining their strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases.
Let’s start with MP3!
MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3)
MP3 is one of the most widely used audio file formats, celebrated for its balance between file size and audio quality.
Key Features:
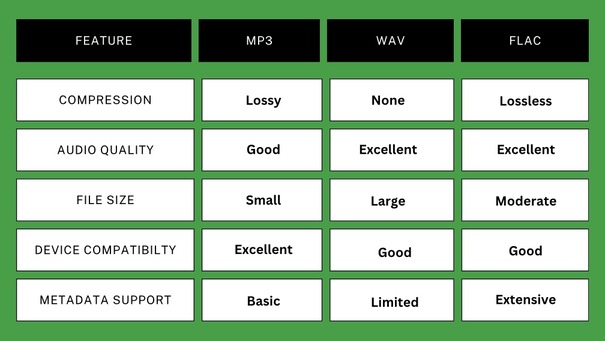
- Compression: MP3 uses lossy compression, which reduces file size by removing inaudible frequencies. This makes it highly portable and efficient for storage.
- Compatibility: Supported by virtually all devices and software, MP3 ensures playback across platforms.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Streaming music on platforms like YouTube.
- Portable storage on devices with limited space, such as smartphones.
- Sharing audio files via email or messaging apps.
Limitations:
- Lossy compression means a loss of audio fidelity compared to original recordings.
- Not suitable for professional audio editing or archiving.
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format)
WAV is a high-quality audio format commonly used in professional environments.
Key Features:
- Uncompressed: WAV files preserve the original audio data without compression, ensuring pristine sound quality.
- Versatile: It can support various codecs, although it is typically used for uncompressed PCM audio.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Professional audio recording and editing.
- Archiving original audio files for preservation.
- Scenarios where high fidelity is non-negotiable, such as film scoring or mastering.
Limitations:
- Large file sizes make it less practical for storage or sharing.
- Limited compatibility with consumer-grade devices compared to MP3.
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC is a popular choice for audiophiles who want the best sound quality without sacrificing storage efficiency.
Key Features:
- Lossless Compression: FLAC reduces file size while retaining the original audio data, offering superior sound quality.
- Metadata Support: Allows embedding detailed information like album art and track details.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Storing and listening to high-resolution music collections.
- Transferring audio files for professional use without quality loss.
- Archiving audio files with reduced storage requirements compared to WAV.
Limitations:
- Larger file sizes than MP3.
- Less universal device compatibility compared to MP3, although this is improving.
Comparing the Audio Formats
Choosing the Right Format
The best audio format depends on your specific needs:
- For everyday listening and sharing: Choose MP3 for its convenience and compatibility.
- For professional editing or high-quality playback: Use WAV to preserve the original sound.
- For audiophile-grade sound and efficient storage: Opt for FLAC to enjoy lossless quality without excessive file sizes.
In Conclusion
Understanding the differences between MP3, WAV, and FLAC empowers you to choose the right format for your audio projects. Whether streaming music, recording audio, or archiving your favorite tracks, selecting the appropriate format ensures an optimal listening and sharing experience.
Use this simple guide to make informed decisions and get the most out of your audio files!